In the forthcoming models, the system consists of one or more CA, and it evolves as a whole. CA[600] is called stem process. It is isolated and does not interact with the environment. The stem plants other processes and controls them. They are generally short lived and called transitory processes which serve as interface between stem and the outside.
In the forthcoming models, the system consists of one or more CA, and it evolves as a whole. CA[600] is called stem process. It is isolated and does not interact with the environment. The stem plants other processes and controls them. They are generally short lived and called transitory processes which serve as interface between stem and the outside. Properties of the Stem
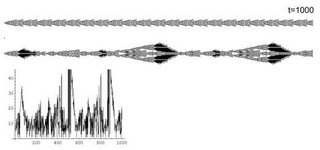
The present experiment depicts a two CA system, a stem CA[600] and a transitory process, CA[2058]. Despite its potential immortality , sooner or later it will be eliminated by the stem and replaced by a another process. The system is continually turning over. Moreover the system proceeds from solution to solution and cannot expand forever. The stem therefore curbs CA[2058]. It is controlled by the stem size. Whenever CA[2058] => k*CA[600], its boundary cells are set to zero. (k , accounts for proportionality) (v. Chapter 10 Injury)
When the stem matures it starts modulating the other CA. Following a transient they start resonating.